Code
library(dplyr)
library(DECIPHER)
library(seqinr)
library(ape)
library(ggplot2)
library(Biostrings)Distance histogram comparisons and detection of small distance pairs
This analysis creates the data we analyse from the SILVA database by taking a random set of 205 sequences to start with, aligning them and choosing the most informative contiguous subsequence of length 450. We take 200 first ones that align correctly and then use those to run the 40/160 cuts many times, we look at the 1st and 5th percentiles. Using the 1st percentil we create a threshold of detection of “very close” species and see that in fact these are all duplicates.
We start by loading the libraries we need, include the Bioconductor package DECIPHER that we use for alignment. To install the Bioconductor package DECIPHER that provides the best alignment function:
BiocManager::install("DECIPHER")We make sure Biostrings is loaded last because of the width function.
The Silva database silva_nr99_v138.2_toGenus_trainset.fa was downloaded from zenodo (DADA2) benchmark dataset.
Originally this file should contain only bacteria, but we will check.
# Step 2: Filter for bacterial sequences and extract taxonomic information
is_bacteria <- grepl("Bacteria;", names(silva_seqs))
bacteria_seqs <- silva_seqs[is_bacteria]
# Extract phylum information
get_phylum <- function(full_taxonomy) {
split_tax <- strsplit(full_taxonomy, ";")[[1]]
return(ifelse(length(split_tax) >= 3, split_tax[3], NA)) # Return NA if phylum level is missing
}
phyla <- sapply(names(bacteria_seqs), get_phylum)
# Step 3: Stratify sampling across phyla
phylum_counts <- table(phyla, useNA = "ifany")
top_phyla <- names(sort(phylum_counts, decreasing = TRUE))
top_phyla <- top_phyla[!is.na(top_phyla)][1:10] # Top 10 phyla, excluding NAWe choose to sample 21 species from the 10 most frequent phyla to create a diverse reference set of about 210 (we’ll discard a few when doing the alignment).
# Step 4: Random sampling
set.seed(2042) # for reproducibility
sampled_seqs <- lapply(top_phyla, function(phylum) {
phylum_indices <- which(phyla == phylum)
if (length(phylum_indices) > n_per_phylum) {
sampled_indices <- sample(phylum_indices, n_per_phylum)
} else {
sampled_indices <- phylum_indices
}
bacteria_seqs[sampled_indices]
})
# Combine sampled sequences
final_sample <- do.call(c, sampled_seqs)
# Ensure we have at least 205 sequences, randomly sampling more if needed
if (length(final_sample) < 205) {
remaining_indices <- which(!names(bacteria_seqs) %in% names(final_sample))
additional_sample <- sample(bacteria_seqs[remaining_indices], 205 -
length(final_sample))
final_sample <- c(final_sample, additional_sample)
}
# Trim to exactly 205 if we have more
final_sample <- final_sample[1:205]
cat("\nSummary of width of sequences chosen:",
summary(Biostrings::width(final_sample)),"\n")
Summary of width of sequences chosen: 1200 1364 1431 1419.634 1482 1870 So the sequences have varying lengths from about 1200 to rmax(Biostrings::width(final_sample))` and we want to find subsequences of length about 450 that can be “aligned” so have a certain number of conserved positions that can be used as anchors and we need variability in the other positions which serve to characterize the different species.
Aligning sequences...aligned_seqs <- AlignSeqs(final_sample, anchor=NA, verbose = FALSE)
# Convert to DNAStringSet for easier manipulation
aligned_seqs_dna <- DNAStringSet(aligned_seqs)
# Function to find the most informative region
find_informative_region <- function(aligned_seqs, target_length = 450, window_size = 50) {
# Create a simple consensus
cons_matrix <- consensusMatrix(aligned_seqs)
consensus <- apply(cons_matrix[c("A", "C", "G", "T"), ], 2, function(x) {
if (sum(x) == 0) return("-")
names(which.max(x))
})
consensus <- paste(consensus, collapse = "")
# Slide a window across the consensus sequence
scores <- sapply(1:(nchar(consensus) - window_size + 1), function(i) {
window <- substr(consensus, i, i + window_size - 1)
sum(window != "-") / window_size # Score based on non-gap content
})
# Find the highest scoring region that's close to the target length
start <- which.max(scores)
end <- min(start + target_length - 1, nchar(consensus))
return(c(start, end))
}
# Find the most informative region
cat("Finding informative region...\n")Finding informative region...region <- find_informative_region(aligned_seqs_dna)
# Extract the region from all sequences
final_aligned_seqs <- subseq(aligned_seqs_dna, start = region[1], end = region[2])
# Create a data frame to store original names and new unique identifiers
sequence_info <- data.frame(
original_name = names(final_aligned_seqs),
unique_id = paste0("Seq_", seq_along(final_aligned_seqs)),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
# Assign unique identifiers as names, but keep original names as attributes
names(final_aligned_seqs) <- sequence_info$unique_id
for (i in seq_along(final_aligned_seqs)) {
attr(final_aligned_seqs[[i]], "original_name") <- sequence_info$original_name[i]
}
# Write the aligned sequences to a file
writeXStringSet(final_aligned_seqs, "../data/test_silva_aligned_bacteria_sequences.fasta")
# Write sequence information to a separate file
write.csv(sequence_info, "../data/test_silva_sequence_info.csv", row.names = FALSE)
# Print summary of the final aligned sequences
cat("\nFinal alignment summary:\n")
Final alignment summary: Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
450 450 450 450 450 450
Number of sequences in final alignment: 205
Alignment characteristics:Conserved positions: 79 Variable positions: 371
Gap proportion in final sequences: Min. 1st Qu. Median Mean 3rd Qu. Max.
0.2467 0.3000 0.3422 0.3524 0.3800 0.7756 Max gap proportion: 0.7755556
Example of sequence names: original_name
1 Bacteria;Pseudomonadota;Gammaproteobacteria;Pseudomonadales;Moraxellaceae;
2 Bacteria;Pseudomonadota;Gammaproteobacteria;Enterobacterales;Enterobacteriaceae;Escherichia-Shigella;
3 Bacteria;Pseudomonadota;Gammaproteobacteria;Pseudomonadales;Pseudomonadaceae;Pseudomonas;
4 Bacteria;Pseudomonadota;Gammaproteobacteria;Burkholderiales;Oxalobacteraceae;Janthinobacterium;
5 Bacteria;Pseudomonadota;Gammaproteobacteria;Pseudomonadales;Halomonadaceae;Halomonas;
6 Bacteria;Pseudomonadota;Gammaproteobacteria;Pseudomonadales;SAR86 clade;
unique_id
1 Seq_1
2 Seq_2
3 Seq_3
4 Seq_4
5 Seq_5
6 Seq_6Now we have the 200 sequences, we can do the simulations by making random splits 40-160 here we use the Kimura distance between DNA sequences.
library(ape)
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
library(Biostrings)
# Read the aligned sequences
aligned_seqs <- readDNAStringSet("../data/silva_aligned_bacteria_sequences.fasta")
# Take the first 200 sequences
aligned_seqs_200 <- aligned_seqs[1:200]
# Convert to DNAbin object (required for dist.dna)
dna_bin <- as.DNAbin(aligned_seqs_200)
# Compute Kimura 2-parameter distances
dist_matrix <- as.matrix(dist.dna(dna_bin, model = "K80", pairwise.deletion = TRUE))
# Function to get nearest neighbor distances
get_nn_distances <- function(dist_matrix, indices) {
nn_distances <- apply(dist_matrix[indices, indices, drop = FALSE], 1, function(row) min(row[row > 0]))
return(nn_distances)
}
# Function to get nearest neighbor distances between two sets
get_nn_distances_between <- function(dist_matrix, from_indices, to_indices) {
nn_distances <- apply(dist_matrix[from_indices, to_indices, drop = FALSE], 1, min)
return(nn_distances)
}
# Perform multiple samplings and collect results
n_simulations <- 1000
sample_size <- 40
within_sample_distances <- list()
between_sample_distances <- list()
set.seed(194501) # for reproducibility
for (i in 1:n_simulations) {
# Random sampling
sample_indices <- sample(1:200, sample_size)
non_sample_indices <- setdiff(1:200, sample_indices)
# Within-sample nearest neighbor distances
within_sample_distances[[i]] <- get_nn_distances(dist_matrix, sample_indices)
# Between sample and population nearest neighbor distances
between_sample_distances[[i]] <- get_nn_distances_between(dist_matrix, non_sample_indices, sample_indices)
}
# Combine results
within_sample_df <- data.frame(
Distance = unlist(within_sample_distances),
Type = "Within Sample"
)
between_sample_df <- data.frame(
Distance = unlist(between_sample_distances),
Type = "Between Sample and Population"
)all_distances_df <- rbind(within_sample_df, between_sample_df)
# Create histograms
all_plot<- ggplot(all_distances_df, aes(x = Distance, fill = Type)) +
geom_histogram(position = "identity", alpha = 0.7, bins = 30) +
facet_wrap(~Type, scales = "free_y", ncol = 1) +
labs(# title = "Distribution of Nearest Neighbor Distances",
x = "Kimura 2-parameter Distance",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal() +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Within Sample" = "blue", "Between Sample and Population" = "red")) +
theme(legend.position = "none",
#axis.title = element_blank(),
plot.title = element_blank())
print(all_plot)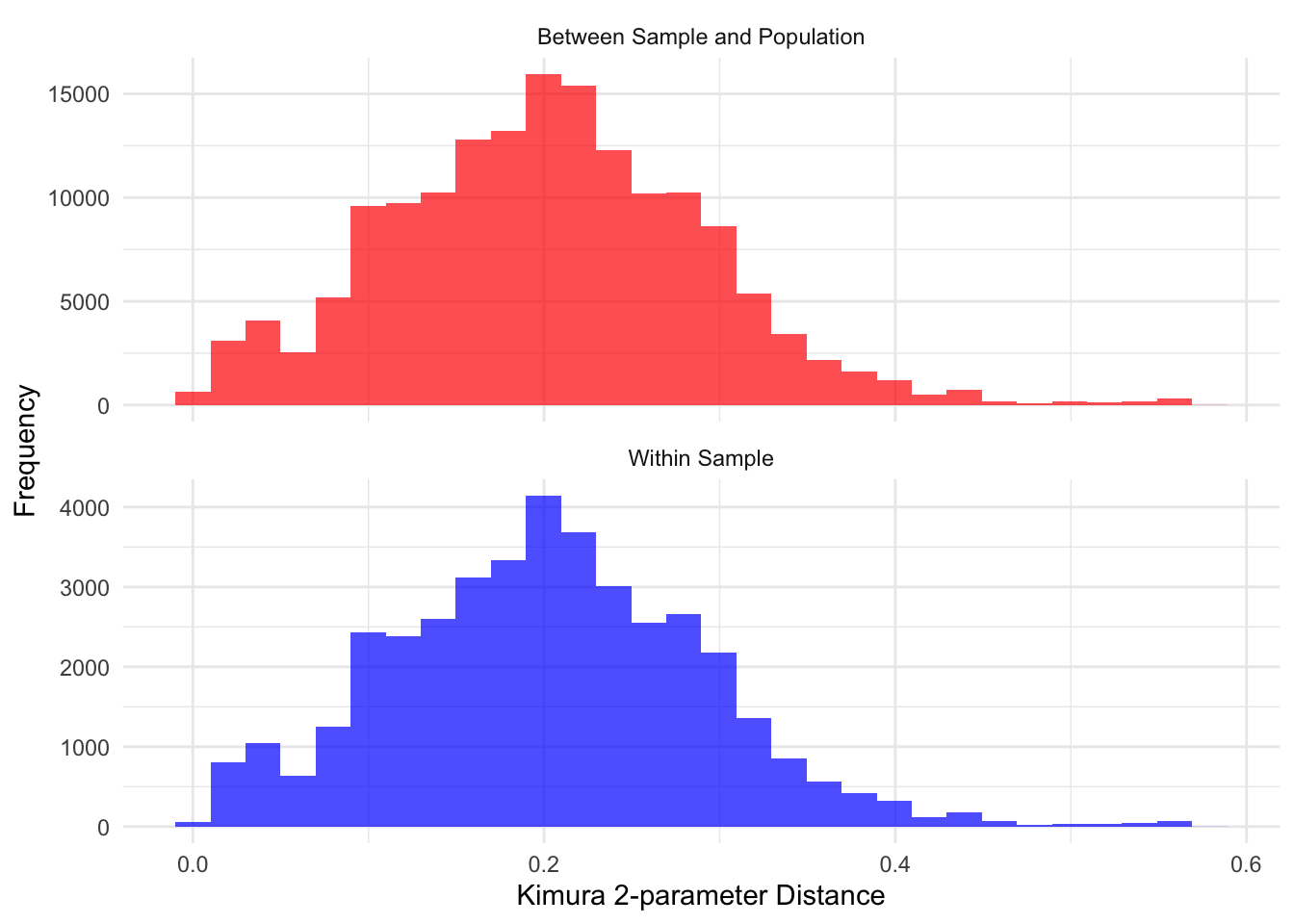
library(gridExtra)
# Function to create histogram without legend or title
create_histogram <- function(data, fill_color) {
ggplot(data.frame(Distance = data), aes(x = Distance)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 30, fill = fill_color, alpha = 0.7) +
labs(# title = "Distribution of Nearest Neighbor Distances",
x = "Kimura 2-parameter Distance",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "none",
#axis.title = element_blank(),
plot.title = element_blank())
}
# Create histograms
hist_within <- create_histogram(unlist(within_sample_distances), "blue")
hist_between <- create_histogram(unlist(between_sample_distances), "red")
# Combine histograms
combined_hist1 <- grid.arrange(hist_within, hist_between, nrow = 2)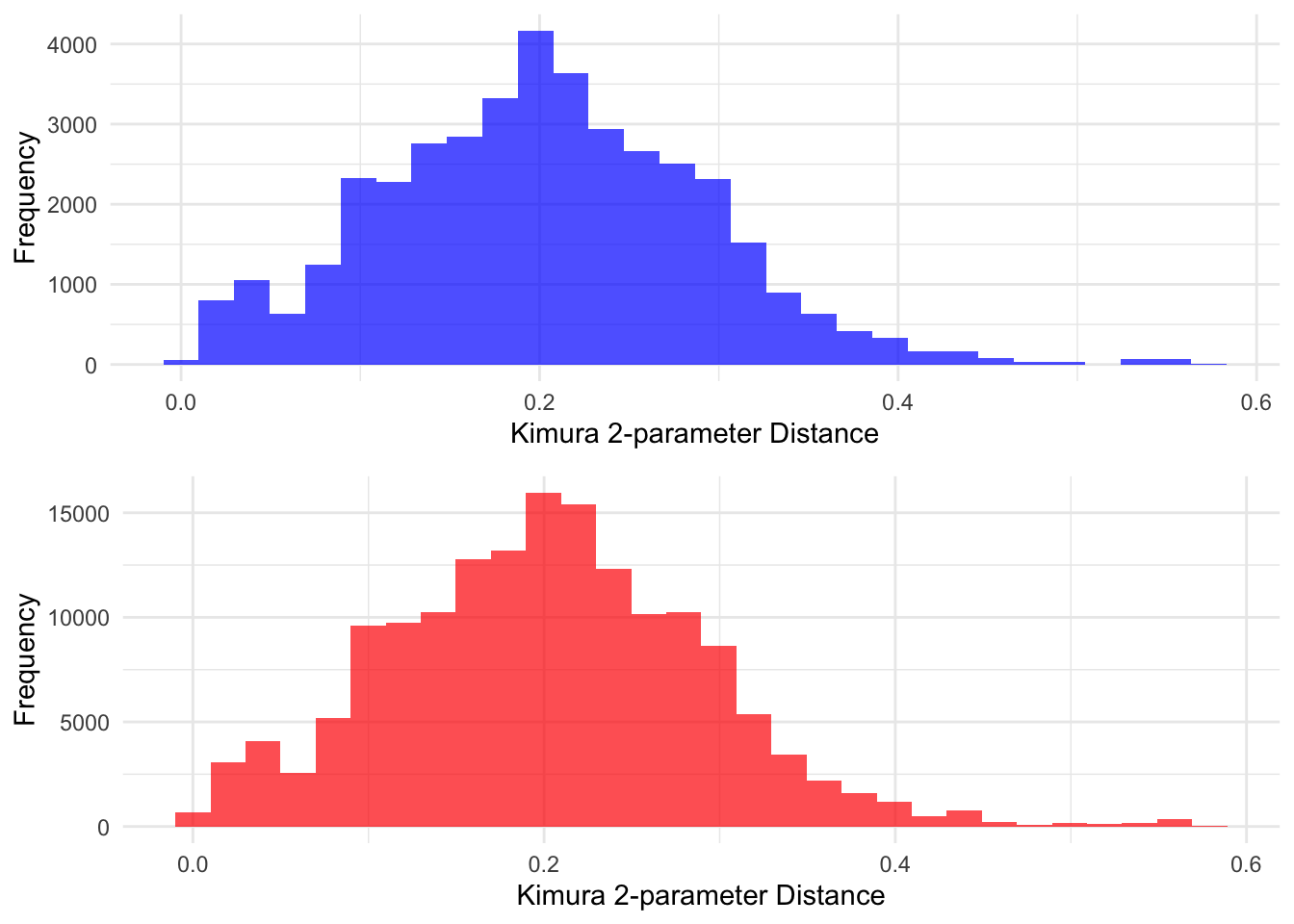
TableGrob (2 x 1) "arrange": 2 grobs
z cells name grob
1 1 (1-1,1-1) arrange gtable[layout]
2 2 (2-2,1-1) arrange gtable[layout]# Function to create histogram with density estimate
create_histogram_with_density <- function(data, fill_color, line_color) {
ggplot(data.frame(Distance = data), aes(x = Distance)) +
geom_histogram(aes(y = ..density..), bins = 30, fill = fill_color, alpha = 0.7) +
geom_density(color = line_color, size = 1, alpha = 0.8,adjust=2) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "none",
axis.title = element_blank(),
plot.title = element_blank())
}
# Create histograms with density estimates
hist_within <- create_histogram_with_density(unlist(within_sample_distances), "blue", "darkblue")
hist_between <- create_histogram_with_density(unlist(between_sample_distances), "red", "darkred")
# Combine histograms
combined_hist2 <- grid.arrange(hist_within, hist_between, nrow = 2)
TableGrob (2 x 1) "arrange": 2 grobs
z cells name grob
1 1 (1-1,1-1) arrange gtable[layout]
2 2 (2-2,1-1) arrange gtable[layout]# Assuming within_sample_distances and between_sample_distances are lists of vectors
# Function to calculate percentiles for a list of distance vectors
calculate_percentiles <- function(distance_list, percentiles) {
all_distances <- unlist(distance_list)
sapply(percentiles, function(p) quantile(all_distances, p/100))
}
# Calculate 1st and 5th percentiles for both distributions
percentiles <- c(1, 5)
within_percentiles <- calculate_percentiles(within_sample_distances, percentiles)
between_percentiles <- calculate_percentiles(between_sample_distances, percentiles)
# Create a data frame for easy comparison
percentile_comparison <- data.frame(
Percentile = c("1st", "5th"),
Within_Sample = within_percentiles,
Sample_to_Population = between_percentiles
)
# Print the comparison
cat("Comparison of 1st and 5th percentiles:\n")Comparison of 1st and 5th percentiles: Percentile Within_Sample Sample_to_Population
1st 0.01548814 0.01460938
5th 0.05423807 0.05096344
Differences (Within Sample - Sample to Population):1st percentile difference: 0.0008787655 5th percentile difference: 0.003274623 # Plot distribution of AD statistics
ad_plot<- ggplot(data.frame(AD_statistic = ad_stats[, "AD_statistic"]), aes(x = AD_statistic)) +
geom_histogram(aes(y = ..density..), fill = "purple", alpha = 0.7, bins = 30) +
geom_density(color="purple")+
geom_density(data = data.frame(stat = ad_stats_null),
aes(x = stat),
color = "blue", size = 1) +
labs(#title = "Distribution of Anderson-Darling Test Statistics",
x = "AD Statistic",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position="none",
plot.title = element_blank())
print(ad_plot)
#ggsave("silva_anderson_darling_histogram.png", ad_plot, width = 5, height = 5)library(ape)
library(ggplot2)
library(Biostrings)
# Read the aligned sequences
aligned_seqs <- readDNAStringSet("../data/silva_aligned_bacteria_sequences.fasta")
# Take the first 200 sequences
aligned_seqs_200 <- aligned_seqs[1:200]
# Read the sequence information
sequence_info <- read.csv("../data/silva_sequence_info.csv", stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
# Create a named vector for easy lookup
name_mapping <- setNames(sequence_info$original_name, sequence_info$unique_id)
# Convert to DNAbin object (required for dist.dna)
dna_bin <- as.DNAbin(aligned_seqs_200)
# Compute Kimura 2-parameter distances
dist_matrix <- as.matrix(dist.dna(dna_bin, model = "K80", pairwise.deletion = TRUE))
# Function to get unique pairs of sequences with distances smaller than the threshold
get_close_pairs <- function(dist_matrix, threshold) {
close_pairs <- which(dist_matrix < threshold & dist_matrix > 0 & lower.tri(dist_matrix), arr.ind = TRUE)
if (nrow(close_pairs) == 0) {
return(NULL)
}
data.frame(
Seq1 = rownames(dist_matrix)[close_pairs[,1]],
Seq2 = colnames(dist_matrix)[close_pairs[,2]],
Distance = dist_matrix[close_pairs]
)
}
# Set the threshold to 0.015488
threshold <- 0.015488
# Get close pairs
close_pairs_df <- get_close_pairs(dist_matrix, threshold)
if (is.null(close_pairs_df)) {
cat("No pairs found with distance smaller than", threshold, "\n")
} else {
cat("Pairs of sequences with distances smaller than", threshold, ":\n\n")
# Print the close pairs with original taxonomic names
for (i in 1:nrow(close_pairs_df)) {
cat("Pair", i, ":\n")
cat("Sequence 1:", name_mapping[close_pairs_df$Seq1[i]], "\n")
cat("Sequence 2:", name_mapping[close_pairs_df$Seq2[i]], "\n")
cat("Distance:", close_pairs_df$Distance[i], "\n\n")
}
cat("Number of unique close pairs found:", nrow(close_pairs_df), "\n")
}Pairs of sequences with distances smaller than 0.015488 :
Pair 1 :
Sequence 1: Bacteria;Bacillota;Bacilli;Staphylococcales;Staphylococcaceae;Staphylococcus;
Sequence 2: Bacteria;Bacillota;Bacilli;Staphylococcales;Staphylococcaceae;Staphylococcus;
Distance: 0.003067494
Pair 2 :
Sequence 1: Bacteria;Actinomycetota;Actinobacteria;Kitasatosporales;Streptomycetaceae;Streptomyces;
Sequence 2: Bacteria;Actinomycetota;Actinobacteria;Kitasatosporales;Streptomycetaceae;Streptomyces;
Distance: 0.01017183
Pair 3 :
Sequence 1: Bacteria;Actinomycetota;Actinobacteria;Propionibacteriales;Propionibacteriaceae;Cutibacterium;
Sequence 2: Bacteria;Actinomycetota;Actinobacteria;Propionibacteriales;Propionibacteriaceae;Cutibacterium;
Distance: 0.01460938
Pair 4 :
Sequence 1: Bacteria;Actinomycetota;Actinobacteria;Propionibacteriales;Propionibacteriaceae;Cutibacterium;
Sequence 2: Bacteria;Actinomycetota;Actinobacteria;Propionibacteriales;Propionibacteriaceae;Cutibacterium;
Distance: 0.01356862
Pair 5 :
Sequence 1: Bacteria;Cyanobacteriota;Cyanobacteriia;Cyanobacteriales;Coleofasciculaceae;Coleofasciculus PCC-7420;
Sequence 2: Bacteria;Cyanobacteriota;Cyanobacteriia;Cyanobacteriales;Coleofasciculaceae;Coleofasciculus PCC-7420;
Distance: 0.01137475
Number of unique close pairs found: 5 # Histogram of all distances
all_distances <- dist_matrix[lower.tri(dist_matrix)]
ggplot(data.frame(Distance = all_distances), aes(x = Distance)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 50, fill = "blue", alpha = 0.7) +
labs(#title = "Distribution of All Pairwise Distances (SILVA)",
x = "Kimura 2-parameter Distance",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal() +
geom_vline(xintercept = threshold, color = "red", linetype = "dashed")
# Save the histogram
# ggsave("silva_all_distances_histogram.png", width = 10, height = 6)library(ggplot2)
# Function to create and save the plot
create_ad_plot <- function(p_values, n1, n2, filename) {
# Calculate 95th and 99th percentiles of the uniform distribution
percentile_95 <- 0.95
percentile_99 <- 0.99
p <- ggplot(data.frame(p_value = p_values), aes(x = p_value)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 30, fill = "skyblue", color = "black", aes(y = ..density..)) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 1, color = "red", linetype = "dashed") + # Uniform distribution line
geom_vline(xintercept = 0.05, color = "red", linetype = "dashed") +
geom_vline(xintercept = percentile_95, color = "green", linetype = "dashed") +
geom_vline(xintercept = percentile_99, color = "blue", linetype = "dashed") +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = c(0, 0.05, percentile_95, percentile_99, 1),
labels = c("0", "0.05", "95th", "99th", "1")) +
labs(x = "Anderson-Darling p-value",
y = "Density",
title = paste("A-D p-values (n1 =", n1, ", n2 =", n2, ")")) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 45, hjust = 1))
ggsave(filename, p, width = 8, height = 6)
# Print summary statistics
cat("For n1 =", n1, "and n2 =", n2, ":\n")
cat("Proportion of p-values < 0.05:", mean(p_values < 0.05), "\n")
cat("Mean p-value:", mean(p_values), "\n")
cat("Median p-value:", median(p_values), "\n\n")
}
# For n1 = 40, n2 = 160
create_ad_plot(ad_results_40_160, 40, 160, "anderson_darling_pvalues_40_160.png")
# For n1 = 100, n2 = 400
# create_ad_plot(ad_results_100_400, 100, 400, "anderson_darling_pvalues_100_400.png")---
title: "Coincidence Detection using Distances: SILVA data"
subtitle: "Distance histogram comparisons and detection of small distance pairs"
execute:
warning: false
message: false
cache: false
---
## Overview
This analysis creates the data we analyse from the SILVA database
by taking a random set of 205 sequences to start with, aligning them
and choosing the most informative contiguous subsequence of length 450.
We take 200 first ones that align correctly and then use those to run the 40/160
cuts many times, we look at the 1st and 5th percentiles.
Using the 1st percentil we create a threshold of detection of "very close"
species and see that in fact these are all duplicates.
## Step 1: Prepare downloaded data from SILVA database
We start by loading the libraries we need, include the Bioconductor package
`DECIPHER` that we use for alignment.
To install the Bioconductor package `DECIPHER`
that provides the best alignment function:
```
BiocManager::install("DECIPHER")
```
We make sure Biostrings is loaded last because of the width function.
The Silva database `silva_nr99_v138.2_toGenus_trainset.fa` was downloaded from
zenodo (DADA2) benchmark dataset.
Originally this file should contain only bacteria, but we will check.
```{r setup}
#| cache: false
#| cache-refresh: true
library(dplyr)
library(DECIPHER)
library(seqinr)
library(ape)
library(ggplot2)
library(Biostrings)
```
```{r loadSILVAintial}
# Step 1: Load the SILVA database
silva_file <- "../data/silva_nr99_v138.2_toGenus_trainset.fa"
silva_seqs <- readDNAStringSet(silva_file)
```
### Among the Bacteria we pick the top 10 phyla
```{r tryphyla, eval=TRUE}
# Step 2: Filter for bacterial sequences and extract taxonomic information
is_bacteria <- grepl("Bacteria;", names(silva_seqs))
bacteria_seqs <- silva_seqs[is_bacteria]
# Extract phylum information
get_phylum <- function(full_taxonomy) {
split_tax <- strsplit(full_taxonomy, ";")[[1]]
return(ifelse(length(split_tax) >= 3, split_tax[3], NA)) # Return NA if phylum level is missing
}
phyla <- sapply(names(bacteria_seqs), get_phylum)
# Step 3: Stratify sampling across phyla
phylum_counts <- table(phyla, useNA = "ifany")
top_phyla <- names(sort(phylum_counts, decreasing = TRUE))
top_phyla <- top_phyla[!is.na(top_phyla)][1:10] # Top 10 phyla, excluding NA
```
We choose to sample 21 species from the 10 most frequent phyla
to create a diverse reference set of about 210 (we'll discard a few
when doing the alignment).
```{r}
# Calculate number of sequences to sample from each phylum
n_per_phylum <- 21 # Increased from 20 to 21 to get 210 sequences (allowing for some potential loss in alignment)
```
### We create the random sample from the 10 main phyla.
```{r}
# Step 4: Random sampling
set.seed(2042) # for reproducibility
sampled_seqs <- lapply(top_phyla, function(phylum) {
phylum_indices <- which(phyla == phylum)
if (length(phylum_indices) > n_per_phylum) {
sampled_indices <- sample(phylum_indices, n_per_phylum)
} else {
sampled_indices <- phylum_indices
}
bacteria_seqs[sampled_indices]
})
# Combine sampled sequences
final_sample <- do.call(c, sampled_seqs)
# Ensure we have at least 205 sequences, randomly sampling more if needed
if (length(final_sample) < 205) {
remaining_indices <- which(!names(bacteria_seqs) %in% names(final_sample))
additional_sample <- sample(bacteria_seqs[remaining_indices], 205 -
length(final_sample))
final_sample <- c(final_sample, additional_sample)
}
# Trim to exactly 205 if we have more
final_sample <- final_sample[1:205]
cat("\nSummary of width of sequences chosen:",
summary(Biostrings::width(final_sample)),"\n")
```
## Step 2: Alignment with penalties
So the sequences have varying lengths from about `r min(width(final_sample))` to
`r `max(Biostrings::width(final_sample))`
and we want to find subsequences of length about 450 that
can be "aligned" so have a certain number of conserved
positions that can be used as anchors and we need variability
in the other positions which serve to characterize the different
species.
```{r alignment,eval=TRUE}
# Align the sequences
cat("Aligning sequences...\n")
aligned_seqs <- AlignSeqs(final_sample, anchor=NA, verbose = FALSE)
# Convert to DNAStringSet for easier manipulation
aligned_seqs_dna <- DNAStringSet(aligned_seqs)
# Function to find the most informative region
find_informative_region <- function(aligned_seqs, target_length = 450, window_size = 50) {
# Create a simple consensus
cons_matrix <- consensusMatrix(aligned_seqs)
consensus <- apply(cons_matrix[c("A", "C", "G", "T"), ], 2, function(x) {
if (sum(x) == 0) return("-")
names(which.max(x))
})
consensus <- paste(consensus, collapse = "")
# Slide a window across the consensus sequence
scores <- sapply(1:(nchar(consensus) - window_size + 1), function(i) {
window <- substr(consensus, i, i + window_size - 1)
sum(window != "-") / window_size # Score based on non-gap content
})
# Find the highest scoring region that's close to the target length
start <- which.max(scores)
end <- min(start + target_length - 1, nchar(consensus))
return(c(start, end))
}
# Find the most informative region
cat("Finding informative region...\n")
region <- find_informative_region(aligned_seqs_dna)
# Extract the region from all sequences
final_aligned_seqs <- subseq(aligned_seqs_dna, start = region[1], end = region[2])
# Create a data frame to store original names and new unique identifiers
sequence_info <- data.frame(
original_name = names(final_aligned_seqs),
unique_id = paste0("Seq_", seq_along(final_aligned_seqs)),
stringsAsFactors = FALSE
)
# Assign unique identifiers as names, but keep original names as attributes
names(final_aligned_seqs) <- sequence_info$unique_id
for (i in seq_along(final_aligned_seqs)) {
attr(final_aligned_seqs[[i]], "original_name") <- sequence_info$original_name[i]
}
# Write the aligned sequences to a file
writeXStringSet(final_aligned_seqs, "../data/test_silva_aligned_bacteria_sequences.fasta")
# Write sequence information to a separate file
write.csv(sequence_info, "../data/test_silva_sequence_info.csv", row.names = FALSE)
# Print summary of the final aligned sequences
cat("\nFinal alignment summary:\n")
print(summary(Biostrings::width(final_aligned_seqs)))
cat("\nNumber of sequences in final alignment:", length(final_aligned_seqs), "\n")
# Print some additional information about the alignment
cat("\nAlignment characteristics:\n")
cons_matrix <- consensusMatrix(final_aligned_seqs)
cat("Conserved positions:", sum(apply(cons_matrix[c("A", "C", "G", "T"), ], 2, function(x) max(x) == sum(x))), "\n")
cat("Variable positions:", sum(apply(cons_matrix[c("A", "C", "G", "T"), ], 2, function(x) sum(x > 0) > 1)), "\n")
# Print information about the gap content in the final sequences
gap_props_final <- rowSums(as.matrix(final_aligned_seqs) == "-") / Biostrings::width(final_aligned_seqs)[1]
cat("\nGap proportion in final sequences:\n")
print(summary(gap_props_final))
cat("Max gap proportion:", max(gap_props_final), "\n")
# Print a few examples of original names and their corresponding unique IDs
cat("\nExample of sequence names:\n")
print(head(sequence_info))
```
## Step 3: Compute the within and between distances and compare the histograms
Now we have the 200 sequences, we can do the simulations
by making random splits 40-160
here we use the Kimura distance between DNA sequences.
```{r Fig9bisrealdata}
library(ape)
library(ggplot2)
library(dplyr)
library(Biostrings)
# Read the aligned sequences
aligned_seqs <- readDNAStringSet("../data/silva_aligned_bacteria_sequences.fasta")
# Take the first 200 sequences
aligned_seqs_200 <- aligned_seqs[1:200]
# Convert to DNAbin object (required for dist.dna)
dna_bin <- as.DNAbin(aligned_seqs_200)
# Compute Kimura 2-parameter distances
dist_matrix <- as.matrix(dist.dna(dna_bin, model = "K80", pairwise.deletion = TRUE))
# Function to get nearest neighbor distances
get_nn_distances <- function(dist_matrix, indices) {
nn_distances <- apply(dist_matrix[indices, indices, drop = FALSE], 1, function(row) min(row[row > 0]))
return(nn_distances)
}
# Function to get nearest neighbor distances between two sets
get_nn_distances_between <- function(dist_matrix, from_indices, to_indices) {
nn_distances <- apply(dist_matrix[from_indices, to_indices, drop = FALSE], 1, min)
return(nn_distances)
}
# Perform multiple samplings and collect results
n_simulations <- 1000
sample_size <- 40
within_sample_distances <- list()
between_sample_distances <- list()
set.seed(194501) # for reproducibility
for (i in 1:n_simulations) {
# Random sampling
sample_indices <- sample(1:200, sample_size)
non_sample_indices <- setdiff(1:200, sample_indices)
# Within-sample nearest neighbor distances
within_sample_distances[[i]] <- get_nn_distances(dist_matrix, sample_indices)
# Between sample and population nearest neighbor distances
between_sample_distances[[i]] <- get_nn_distances_between(dist_matrix, non_sample_indices, sample_indices)
}
# Combine results
within_sample_df <- data.frame(
Distance = unlist(within_sample_distances),
Type = "Within Sample"
)
between_sample_df <- data.frame(
Distance = unlist(between_sample_distances),
Type = "Between Sample and Population"
)
```
### Show the histograms of both nn distances
```{r visualizeboth}
all_distances_df <- rbind(within_sample_df, between_sample_df)
# Create histograms
all_plot<- ggplot(all_distances_df, aes(x = Distance, fill = Type)) +
geom_histogram(position = "identity", alpha = 0.7, bins = 30) +
facet_wrap(~Type, scales = "free_y", ncol = 1) +
labs(# title = "Distribution of Nearest Neighbor Distances",
x = "Kimura 2-parameter Distance",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal() +
scale_fill_manual(values = c("Within Sample" = "blue", "Between Sample and Population" = "red")) +
theme(legend.position = "none",
#axis.title = element_blank(),
plot.title = element_blank())
print(all_plot)
#ggsave("silva_nearest_neighbor_distances_histogram.png", all_distances_df , width = 6, height = 4)
```
```{r separatehist}
library(gridExtra)
# Function to create histogram without legend or title
create_histogram <- function(data, fill_color) {
ggplot(data.frame(Distance = data), aes(x = Distance)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 30, fill = fill_color, alpha = 0.7) +
labs(# title = "Distribution of Nearest Neighbor Distances",
x = "Kimura 2-parameter Distance",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "none",
#axis.title = element_blank(),
plot.title = element_blank())
}
# Create histograms
hist_within <- create_histogram(unlist(within_sample_distances), "blue")
hist_between <- create_histogram(unlist(between_sample_distances), "red")
# Combine histograms
combined_hist1 <- grid.arrange(hist_within, hist_between, nrow = 2)
print(combined_hist1)
# Save combined histogram
ggsave("silva_combined_distances_histogram.png", combined_hist1, width = 5, height = 5)
```
```{r densityhisto}
# Function to create histogram with density estimate
create_histogram_with_density <- function(data, fill_color, line_color) {
ggplot(data.frame(Distance = data), aes(x = Distance)) +
geom_histogram(aes(y = ..density..), bins = 30, fill = fill_color, alpha = 0.7) +
geom_density(color = line_color, size = 1, alpha = 0.8,adjust=2) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position = "none",
axis.title = element_blank(),
plot.title = element_blank())
}
# Create histograms with density estimates
hist_within <- create_histogram_with_density(unlist(within_sample_distances), "blue", "darkblue")
hist_between <- create_histogram_with_density(unlist(between_sample_distances), "red", "darkred")
# Combine histograms
combined_hist2 <- grid.arrange(hist_within, hist_between, nrow = 2)
print(combined_hist2)
# Save combined histogram
# ggsave("silva_combined_dist_hist_density.png", combined_hist2, width = 10, height = 5)
```
## Step 4: Using distribution percentiles to find the threshold of "coincidence"
```{r}
# Assuming within_sample_distances and between_sample_distances are lists of vectors
# Function to calculate percentiles for a list of distance vectors
calculate_percentiles <- function(distance_list, percentiles) {
all_distances <- unlist(distance_list)
sapply(percentiles, function(p) quantile(all_distances, p/100))
}
# Calculate 1st and 5th percentiles for both distributions
percentiles <- c(1, 5)
within_percentiles <- calculate_percentiles(within_sample_distances, percentiles)
between_percentiles <- calculate_percentiles(between_sample_distances, percentiles)
# Create a data frame for easy comparison
percentile_comparison <- data.frame(
Percentile = c("1st", "5th"),
Within_Sample = within_percentiles,
Sample_to_Population = between_percentiles
)
# Print the comparison
cat("Comparison of 1st and 5th percentiles:\n")
print(percentile_comparison, row.names = FALSE)
# Calculate and print the differences
cat("\nDifferences (Within Sample - Sample to Population):\n")
diff_1st <- within_percentiles[1] - between_percentiles[1]
diff_5th <- within_percentiles[2] - between_percentiles[2]
cat("1st percentile difference:", diff_1st, "\n")
cat("5th percentile difference:", diff_5th, "\n")
```
```{r ADplot2, eval=FALSE}
# Plot distribution of AD statistics
ad_plot<- ggplot(data.frame(AD_statistic = ad_stats[, "AD_statistic"]), aes(x = AD_statistic)) +
geom_histogram(aes(y = ..density..), fill = "purple", alpha = 0.7, bins = 30) +
geom_density(color="purple")+
geom_density(data = data.frame(stat = ad_stats_null),
aes(x = stat),
color = "blue", size = 1) +
labs(#title = "Distribution of Anderson-Darling Test Statistics",
x = "AD Statistic",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal() +
theme(legend.position="none",
plot.title = element_blank())
print(ad_plot)
#ggsave("silva_anderson_darling_histogram.png", ad_plot, width = 5, height = 5)
```
```{r closecalls}
library(ape)
library(ggplot2)
library(Biostrings)
# Read the aligned sequences
aligned_seqs <- readDNAStringSet("../data/silva_aligned_bacteria_sequences.fasta")
# Take the first 200 sequences
aligned_seqs_200 <- aligned_seqs[1:200]
# Read the sequence information
sequence_info <- read.csv("../data/silva_sequence_info.csv", stringsAsFactors = FALSE)
# Create a named vector for easy lookup
name_mapping <- setNames(sequence_info$original_name, sequence_info$unique_id)
# Convert to DNAbin object (required for dist.dna)
dna_bin <- as.DNAbin(aligned_seqs_200)
# Compute Kimura 2-parameter distances
dist_matrix <- as.matrix(dist.dna(dna_bin, model = "K80", pairwise.deletion = TRUE))
# Function to get unique pairs of sequences with distances smaller than the threshold
get_close_pairs <- function(dist_matrix, threshold) {
close_pairs <- which(dist_matrix < threshold & dist_matrix > 0 & lower.tri(dist_matrix), arr.ind = TRUE)
if (nrow(close_pairs) == 0) {
return(NULL)
}
data.frame(
Seq1 = rownames(dist_matrix)[close_pairs[,1]],
Seq2 = colnames(dist_matrix)[close_pairs[,2]],
Distance = dist_matrix[close_pairs]
)
}
# Set the threshold to 0.015488
threshold <- 0.015488
# Get close pairs
close_pairs_df <- get_close_pairs(dist_matrix, threshold)
if (is.null(close_pairs_df)) {
cat("No pairs found with distance smaller than", threshold, "\n")
} else {
cat("Pairs of sequences with distances smaller than", threshold, ":\n\n")
# Print the close pairs with original taxonomic names
for (i in 1:nrow(close_pairs_df)) {
cat("Pair", i, ":\n")
cat("Sequence 1:", name_mapping[close_pairs_df$Seq1[i]], "\n")
cat("Sequence 2:", name_mapping[close_pairs_df$Seq2[i]], "\n")
cat("Distance:", close_pairs_df$Distance[i], "\n\n")
}
cat("Number of unique close pairs found:", nrow(close_pairs_df), "\n")
}
```
```{r completedist, eval=FALSE}
# Histogram of all distances
all_distances <- dist_matrix[lower.tri(dist_matrix)]
ggplot(data.frame(Distance = all_distances), aes(x = Distance)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 50, fill = "blue", alpha = 0.7) +
labs(#title = "Distribution of All Pairwise Distances (SILVA)",
x = "Kimura 2-parameter Distance",
y = "Frequency") +
theme_minimal() +
geom_vline(xintercept = threshold, color = "red", linetype = "dashed")
# Save the histogram
# ggsave("silva_all_distances_histogram.png", width = 10, height = 6)
```
```{r newadplot,eval=FALSE}
library(ggplot2)
# Function to create and save the plot
create_ad_plot <- function(p_values, n1, n2, filename) {
# Calculate 95th and 99th percentiles of the uniform distribution
percentile_95 <- 0.95
percentile_99 <- 0.99
p <- ggplot(data.frame(p_value = p_values), aes(x = p_value)) +
geom_histogram(bins = 30, fill = "skyblue", color = "black", aes(y = ..density..)) +
geom_hline(yintercept = 1, color = "red", linetype = "dashed") + # Uniform distribution line
geom_vline(xintercept = 0.05, color = "red", linetype = "dashed") +
geom_vline(xintercept = percentile_95, color = "green", linetype = "dashed") +
geom_vline(xintercept = percentile_99, color = "blue", linetype = "dashed") +
scale_x_continuous(breaks = c(0, 0.05, percentile_95, percentile_99, 1),
labels = c("0", "0.05", "95th", "99th", "1")) +
labs(x = "Anderson-Darling p-value",
y = "Density",
title = paste("A-D p-values (n1 =", n1, ", n2 =", n2, ")")) +
theme_minimal() +
theme(axis.text.x = element_text(angle = 45, hjust = 1))
ggsave(filename, p, width = 8, height = 6)
# Print summary statistics
cat("For n1 =", n1, "and n2 =", n2, ":\n")
cat("Proportion of p-values < 0.05:", mean(p_values < 0.05), "\n")
cat("Mean p-value:", mean(p_values), "\n")
cat("Median p-value:", median(p_values), "\n\n")
}
# For n1 = 40, n2 = 160
create_ad_plot(ad_results_40_160, 40, 160, "anderson_darling_pvalues_40_160.png")
# For n1 = 100, n2 = 400
# create_ad_plot(ad_results_100_400, 100, 400, "anderson_darling_pvalues_100_400.png")
```